This script (intended for use on Windows 2003 Server) uses WMI to enumerate the set of running instances of w3wp.exe and, for each, displays which app pool that copy of w3wp.exe is hosting and the corresponding w3wp.exe process ID.
Here's what the output looks like:
C:\>apdump Microsoft (R) Windows Script Host Version 5.6 Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation 1996-2001. All rights reserved. QuickStartV20AppPool (2860) MSSharePointAppPool (3268) DefaultAppPool (3652)
Click here to view the source or here to download the script.
Based on the apdump script above, this script (also intended for use on Windows 2003 Server) uses WMI to enumerate the set of running instances of w3wp.exe and, for each, displays which app pool that copy of w3wp.exe is hosting. But this script then launches the VS.NET JIT debugger with a command line that instructs it to attach to the instance of w3wp.exe that's hosting the app pool you'd like to debug (the name of which is passed as a command line argument to this script).
Here's what the output looks like when you specify the name of an app pool that's not active:
C:\>apdebug NoSuchAppPool Microsoft (R) Windows Script Host Version 5.6 Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation 1996-2001. All rights reserved. Active app pools... QuickStartV20AppPool (2860) MSSharePointAppPool (3268) DefaultAppPool (3652) The app pool specified (NoSuchAppPool) is not running.
And here's what the output looks like when you specify an active app pool name:
C:\>apdebug QuickStartV20AppPool Microsoft (R) Windows Script Host Version 5.6 Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation 1996-2001. All rights reserved. Active app pools... QuickStartV20AppPool (2860) MSSharePointAppPool (3268) DefaultAppPool (3652) Launching debugger for 'QuickStartV20AppPool' (2860)...
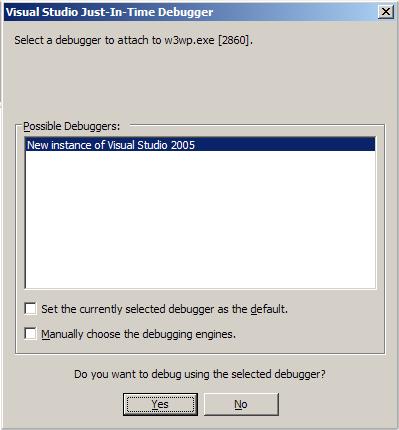
On staging servers where I tend to do nothing but debug a particular service or app, I stick a shortcut on the desktop that runs the script with the name of the target app pool ready to go.
Click here to view the source or here to download the script.
Notes: The prebuilt binary requires the VS.NET runtime libraries on the target system, but the VS.NET and VC6 project files are included along with the source so that you can build the utility to suit.
Platform(s)
Supported: Windows NT 4, Windows 2000 (version
1.0.0.158 and newer).
Notes: Requires administrator privileges
to operate. This utility also requires the Unicode
version of MFC (MFC42U.DLL). If you don't already have
that DLL, or you have an older version, you can download
it here.
Platform(s)
Supported: Windows NT 4, Windows 2000.
Notes: CleanVC.txt
As an Add-In, it operates in the background automatically and can be enabled or disabled, and configured, on a project-by-project basis. Once you enable BuildNum for a specific project, you don't have to do anything manually - it automatically updates the build number header file and your VERSIONINFO recourse each time you build that project.
Changes to 8/29/2001 upload (version 2.0.0.189): BuildNum now first looks for and updates a VERSIONINFO resource in the following prioritized list of places:
- <ProjectDir>\res\<ProjectName>.rc2
- <ProjectDir>\<ProjectName>.rc2
- <ProjectDir>\<ProjectName>.rc
Platform(s) Supported: Any platform
supported by Visual C++ 5.0 or 6.0.
Notes: none.
Usage
is:
cmdline ProcessID
Example:
c:\> cmdline 444
c:\winnt\system32\svchost -k
rpcss
Platform(s) Supported: Windows NT 4,
Windows 2000.
Notes: Requires administrator privileges
to operate.
Source: click here.
Hard Link Source
This feature is only available on volumes formatted with the NTFS file system version 5.0 (or greater) that is used by Windows 2000.
Unlike shortcuts, hard links are first class citizens in NTFS. A hard link is just an alias filename for a file on disk. Any change to the hard link is reflected in the original target file that the link refers to. This includes changes to the contents of the file, as well as attributes of the file (like read-only, etc). You delete a link just like you would delete any file in the file system. Only when the last link to a file has been deleted (including the "original" file name) is the underlying file object removed from the volume.
To install this utility, download the EXE file to any location on your hard drive, and then execute "HardLink /regserver".
To uninstall this utility, execute "HardLink /unregserver", then manually delete the EXE file from your hard drive.
Version 1.0.0.46 (or newer) supports both the shell interface (right click in a directory, select New/Hard Link) as well as a command-line interface that can be invoked directory from a command prompt or command script. Command line syntax is HardLink.exe /l:linkfilename /t:targetfilename. Where linkfilename is the hard link alias to create and targetfilename is the existing file on disk the link should refer to.
Platform(s) Supported: Windows 2000.
Notes: Requires volume(s) to be
formatted with NTFS 5.
Find Links Source
Platform(s)
Supported: Windows NT 4, Windows 2000.
Notes: Require volume(s) to be formatted
with NTFS.
Batch Link Source
Platform(s)
Supported: Windows 2000.
Notes: Requires volume(s) to be
formatted with NTFS 5.